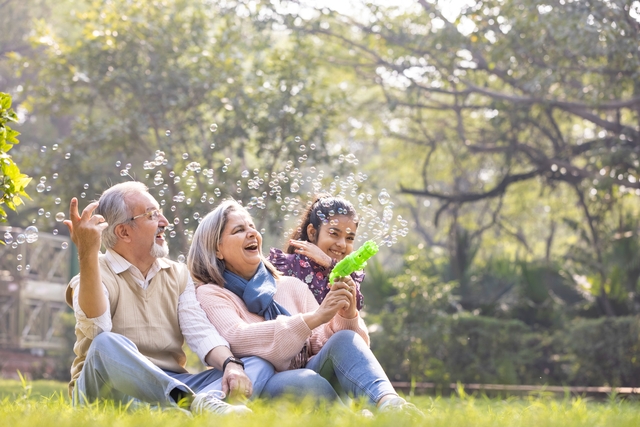
Watching your children frolic through a playground is one of the many joys of being a parent or grandparent, but new research has found that engaging in play with kids could help improve mental health.
Researchers from the University of South Australia (UniSA) and the University of Canberra (UC) have explored the benefits of intergenerational play through specially designed playgrounds for kids and adults.
Intergenerational play brings young children and older people together to engage in enjoyable and creative activities such as storytelling, using playground equipment, and games.
The world is facing an aging population, with the proportion of over 60-year-olds set to double and over 80-year-olds set to triple by 2050.
Associate professor and deputy director of the Australian Research Centre for Interactive and Virtual Environments (IVE) at UniSA, Fanke Peng, says that society needs more public spaces that enable generational integration and interaction.
“There’s a social divide between older and younger people, and it leaves little room for meaningful interaction outside of families and classrooms,” she says.
“This age-based segregation causes feelings of isolation and social disconnectedness, which in turn can lead to depression, anxiety, suicidal ideation, and cognitive decline in older adults.
“The facilitation of a playground designed for children and their parents and grandparents will foster intergenerational play and lead to positive mental health outcomes.”
Assoc Prof Peng says there are barriers that exist that make it harder for older people to engage in play, such as social attitudes and stigmas that play is only for children.
Removing these barriers is crucial in encouraging interaction between generations, and helping to address mental health concerns as people age, she says.