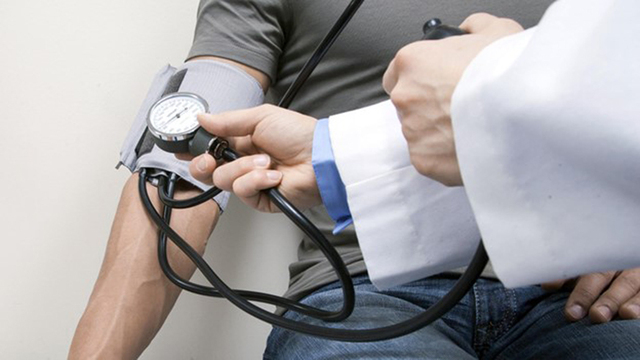
High blood pressure, medically known as hypertension, poses a significant threat to cardiovascular health, particularly for individuals with pre-existing heart conditions. Often referred to as the “silent killer,” hypertension is a silent but potent risk factor for heart attacks, strokes, and other cardiovascular events. In this comprehensive guide, we delve into the importance of maintaining steady blood pressure for cardiac patients and explore actionable
strategies to achieve optimal blood pressure control.
Understanding the Importance
1. Heart Health Connection:
The heart plays a pivotal role in pumping oxygen-rich blood to every part of the body through a network of arteries. Elevated blood pressure strains arteries, heart, causing complications like stiffness and narrowing, increasing cardiac strain and risk of complications.
● Coronary Artery Disease (CAD): Hypertension contributes to the formation of plaque in the arteries, narrowing them and reducing blood flow to the heart. This can lead to angina (chest pain) and increase the risk of heart attacks.
● Heart Failure: Over time, the strain of pumping against high blood pressure weakens the heart, and can ultimately lead to heart failure.
2. Risk Reduction:
Maintaining steady blood pressure is paramount for reducing the risk of life-threatening cardiovascular events. Lowering blood pressure through lifestyle modifications and, when necessary, medication, significantly decreases the likelihood of:
● Heart Attacks: High blood pressure damages the arterial walls, making them susceptible to plaque buildup and rupture. This can lead to the formation of blood clots that block blood flow to the heart, resulting in a heart attack.
● Strokes: Hypertension is a leading cause of ischemic strokes, which occur when a blood clot blocks an artery supplying blood to the brain. Uncontrolled high blood pressure can also cause hemorrhagic strokes, where a weakened blood vessel ruptures, leading to bleeding in the brain.
3. Preserving Organ Function:
Steady blood pressure is essential for preserving the function of vital organs, including the heart, brain, and kidneys. Consistently elevated blood pressure can damage these organs over time, leading to:
● Heart Damage: Chronic hypertension places strain on the heart, compromising its ability to pump blood efficiently, leading to heart failure.
● Brain Damage: High blood pressure damages the delicate blood vessels in the brain, increasing the risk of cognitive decline, vascular dementia, and Alzheimer’s disease.
● Kidney Damage: Hypertension damages the kidneys’ filtering units (nephrons), impairing their function and potentially leading to chronic kidney disease and kidney failure.
Tips for Maintaining Steady Blood Pressure
1. Healthy Diet:
A heart-healthy diet is a cornerstone of blood pressure management.
Emphasize:
● Fruits and Vegetables: Rich in vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants, fruits and vegetables help lower blood pressure and reduce the risk of heart disease.
● Whole Grains: Oats, brown rice, and quinoa, provide fiber and nutrients that support heart health and regulate blood pressure.
● Lean Proteins: Lean sources of protein, such as poultry, fish, legumes, and tofu, which are high in saturated fat and sodium.
● Healthy Fats: Olive oil, avocados, nuts, and seeds, which can help lower cholesterol levels and improve cardiovascular health.
2. Regular Exercise:
Physical activity is crucial for maintaining cardiovascular health and controlling blood pressure.
Aim for:
● Aerobic Exercise: Engage in moderate-intensity aerobic activities, such as brisk walking, cycling, swimming, or dancing, for at least 150 minutes per week.
● Flexibility and Balance: Include flexibility and balance exercises, such as yoga or tai chi, to enhance joint mobility, stability, and relaxation.
3. Weight Management:
Maintaining a healthy weight is essential for blood pressure control and overall cardiovascular health. Focus on calorie and portion control, monitor weight and adjust diet for weight loss.
4. Stress Reduction:
Chronic stress can contribute to elevated blood pressure and increase the risk of cardiovascular events. Incorporate mindful meditation and deep breathing exercises into your daily routine
5. Medication Adherence:
Lifestyle changes might not always suffice for blood pressure control. If prescribed medication, adhere to dosage and attend regular check-ups.
Maintaining steady blood pressure is crucial for heart health. Adopting a heart-healthy lifestyle, including balanced diet, exercise, stress management, and medication adherence, is essential for managing blood pressure in individuals with heart conditions.
For further information regarding Blood pressure management, call (03) 9702 9300 or book online at https://betterhealthfamilyclinic.com.au/contact/online-booking.